AWS Lambda functions are a great way to run some code on a trigger/schedule without needing a whole server dedicated to it. They can be cost effective, but be careful depending on how long they run, and the number of executions per hour, they can be quite costly as well.
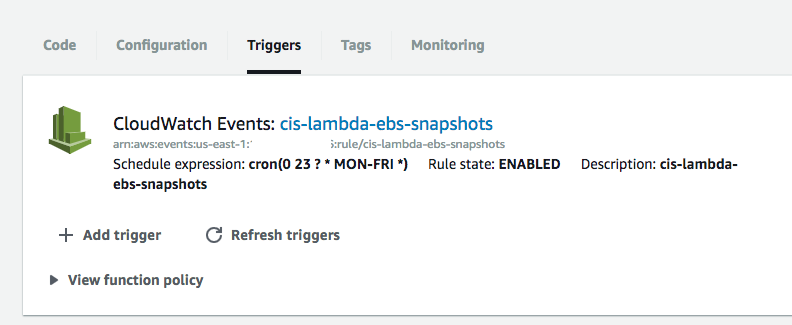
For my use case, I wanted to create snapshot backups of EBS volumes for a Mongo Database every day. I originally implemented this using only CloudWatch, which is a monitoring service, but because it’s focused on scheduling, AWS also uses it for other things that require scheduling/cron like features. Unfortunately, the CloudWatch implementation of snapshot backups was very limited. I could not ‘tag’ the backups, which was certainly something I needed for easy finding and cleanups later (past a retention period).
Anyway, there were a couple pitfalls I ran into when creating this function.
Pitfalls
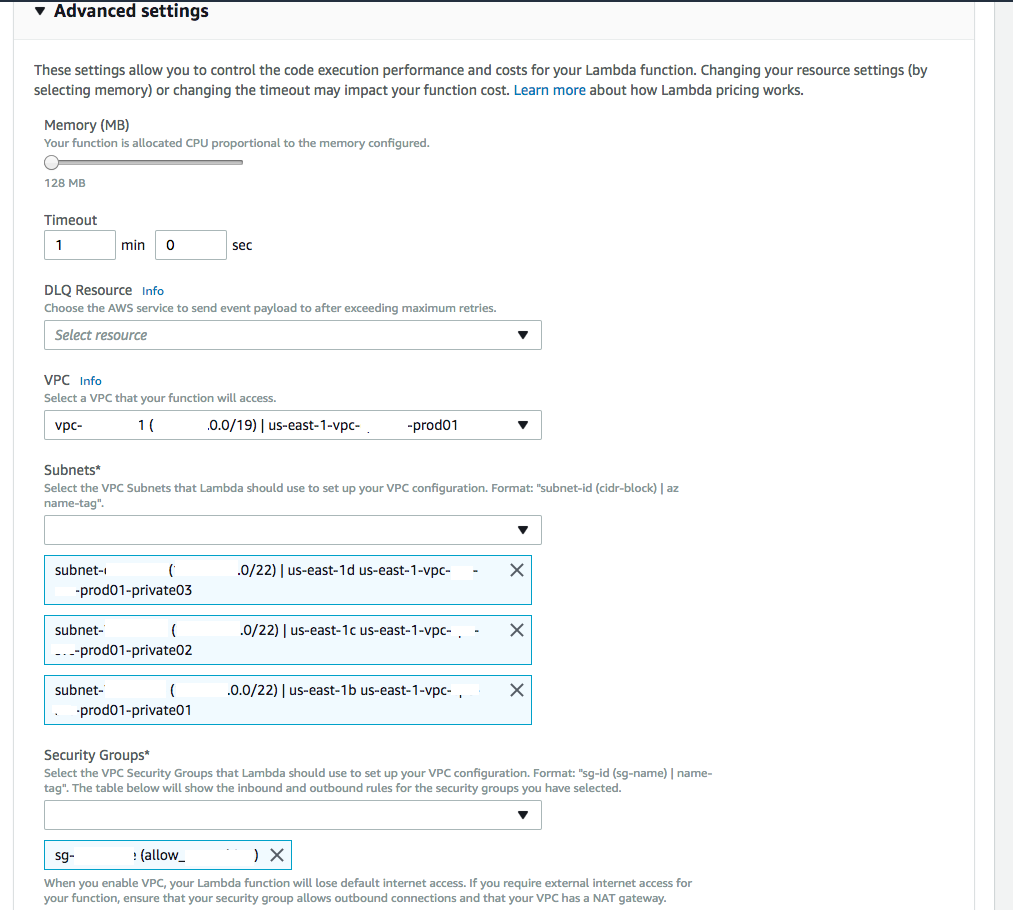
- Make sure you security group allows you to communicate to the Internet for any AWS API’s you need to talk to.
- Make sure your time-out is set to 1 minute or greater depending on your use case. The default is seconds, and is likely not high enough.
- “The Lambda function execution role must have permissions to create, describe and delete ENIs. AWS Lambda provides a permissions policy,
AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole, with permissions for the necessary EC2 actions (ec2:CreateNetworkInterface,ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces, andec2:DeleteNetworkInterface) that you can use when creating a role”- Personally, I did inline permissions and included the specific actions.
- Upload your zip file and make sure your handler section is configured with the exact file_name.method_in_your_code_for_the_handler
- Also this one is more of an FYI, Lambda Function have a maximum TTL of 5 minutes ( 300 seconds).
I think that was it, after that everything worked fine. To finish this short article off, screenshots and the code!
Screenshots
And finally the code…
Function Code
# Backup cis volumes
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
reg = 'us-east-1'
# Connect to region
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=reg)
response = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=[{'Name': 'instance-state-name', 'Values': ['running']},
{'Name': 'tag-key', 'Values': ['Name']},
{'Name': 'tag-value', 'Values': ['cis-mongo*']},
])
for r in response['Reservations']:
for i in r['Instances']:
for mapping in i['BlockDeviceMappings']:
volId = mapping['Ebs']['VolumeId']
# Create snapshot
result = ec2.create_snapshot(VolumeId=volId,
Description='Created by Lambda backup function ebs-snapshots')
# Get snapshot resource
ec2resource = boto3.resource('ec2', region_name=reg)
snapshot = ec2resource.Snapshot(result['SnapshotId'])
# Add volume name to snapshot for easier identification
snapshot.create_tags(Tags=[{'Key': 'Name', 'Value': 'cis-mongo-snapshot-backup'}])
And here is an additional function to add for cleanup
import boto3
from datetime import timedelta, datetime
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# if older than days delete
days = 14
filters = [{'Name': 'tag:Name', 'Values': ['cis-mongo-snapshot-backup']}]
ec2 = boto3.setup_default_session(region_name='us-east-1')
client = boto3.client('ec2')
snapshots = client.describe_snapshots(Filters=filters)
for snapshot in snapshots["Snapshots"]:
start_time = snapshot["StartTime"]
delete_time = datetime.now(start_time.tzinfo) - timedelta(days=days)
if start_time < delete_time:
print 'Deleting {id}'.format(id=snapshot["SnapshotId"])
client.delete_snapshot(SnapshotId=snapshot["SnapshotId"], DryRun=False)
The end, happy server-lessing (ha !)