Overview
In this tutorial I will be demonstrating how to install The Foreman on the Linux CentOS 6.5 operating system. If you are not familiar with CentOS it is the Community version of RedHat Linux Enterprise, hence the name C(ommunity)ENT(erprise) O(perating)S(ystem). For more information on CentOS see : https://www.centos.org/. I chose CentOS over Ubuntu or other Linux flavors for this set of tutorials because of it’s ubiquity in enterprise environments and because of RedHat’s leadership in the Openstack ecosystem. We will discuss Openstack (www.openstack.org) in later tutorials, for now The Foreman represents a great first step to setting up a world class Cloud environment.
Why The Foreman
“Foreman is an open source project that helps system administrators manage servers throughout their lifecycle, from provisioning and configuration to orchestration and monitoring. Using Puppet or Chef and Foreman’s smart proxy architecture, you can easily automate repetitive tasks, quickly deploy applications, and proactively manage change, both on-premise with VMs and bare-metal or in the cloud.” From their website (www.theforeman.org).
In other words it builds on well known configuration management systems (puppet in our case) and fully automates ‘things’ to provision and manage bare metal (physical) systems and Cloud Virtual Machines. This is really helpful when you have an Openstack Cloud and need to add compute nodes quickly.
Starting The Install
My 3 machines in my lab, diamond, ruby and emerald are all running CentOS 6.5. To make sure I cover all the dependencies needed I did a minimal install on these machines. So you will see me install some convenience dependencies as well, which I will point out. The following steps are based loosely on the http://theforeman.org/manuals/1.5/quickstart_guide.html
You will want to install The Foreman on your ‘master’ or machine you intend to the be the ‘controller’ of your Cloud. In my case, diamond.tuxlabs.com
Installing Basic System Dependencies
yum install -y openssh-clients yum install -y yum-utils yum install scl-utils scl-utils-build yum install -y wget yum install -y bind-utils
scl-utils is used for managing the rails console, the rest should be pretty self explanatory.
Installing Foreman Dependencies
wget https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Add Yum Repos
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-6-server-optional-rpms rhel-server-rhscl-6-rpms
Check to make sure the Repo was added using
yum repolist
Installing The Foreman
yum -y install http://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.5/el6/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm yum -y install foreman-installer
After grabbing the packages…finally…run the installer
foreman-installer
This part is pretty cool because foreman’s automated installer seems to work quite well, it takes a few minutes, but when completed you should see something like this.
Preparing installation Done
Success!
* Foreman is running at https://diamond.tuxlabs.com
Default credentials are 'admin:changeme'
* Foreman Proxy is running at https://diamond.tuxlabs.com:8443
* Puppetmaster is running at port 8140
The full log is at /var/log/foreman-installer/foreman-installer.log
[root@diamond tuxninja]#
Iptables
If you have iptables running, you will have to flush the rules or open the need ports.
iptables --flush
Puppet
At this point Puppet should be installed on diamond (and your machine). You should test it by running the agents twice, yes twice 🙂 The first time clears some warnings.
puppet agent --test puppet agent --test
Follow the instructions for installing the NTP module in Puppet
http://theforeman.org/manuals/1.5/index.html#2.2PuppetManagement
I could have re-wrote this or cropped it, but it was written very simply. Definitely do this though so you get a feel for how to add puppet modules and manage them in The Foreman.
The Clients
Now before we get into The Foreman Dashboard, let’s setup our clients so we have more interesting stuff to look at then this one node. ssh to each of your machines (ruby,emerald in my case), and sudo or become root and run…
rpm -ivh http://yum.puppetlabs.com/el/6.4/products/x86_64/puppetlabs-release-6-7.noarch.rpm yum install -y puppet
Then start puppet
/etc/init.d/puppet start
Sign The Certs
Puppet uses SSL certificates to authenticate clients that it manages. By default you must permit each client by manually signing the certificate before the client is authenticated with the puppet master. Back on the master server (diamond) run the following modified for the correct FQDN’s (full hostnames).
puppet cert --sign ruby.tuxlabs.com puppet cert --sign emerald.tuxlabs.com
Auto Starting
Make sure Puppet starts on boot, do this on all machines
chkconfig puppet on
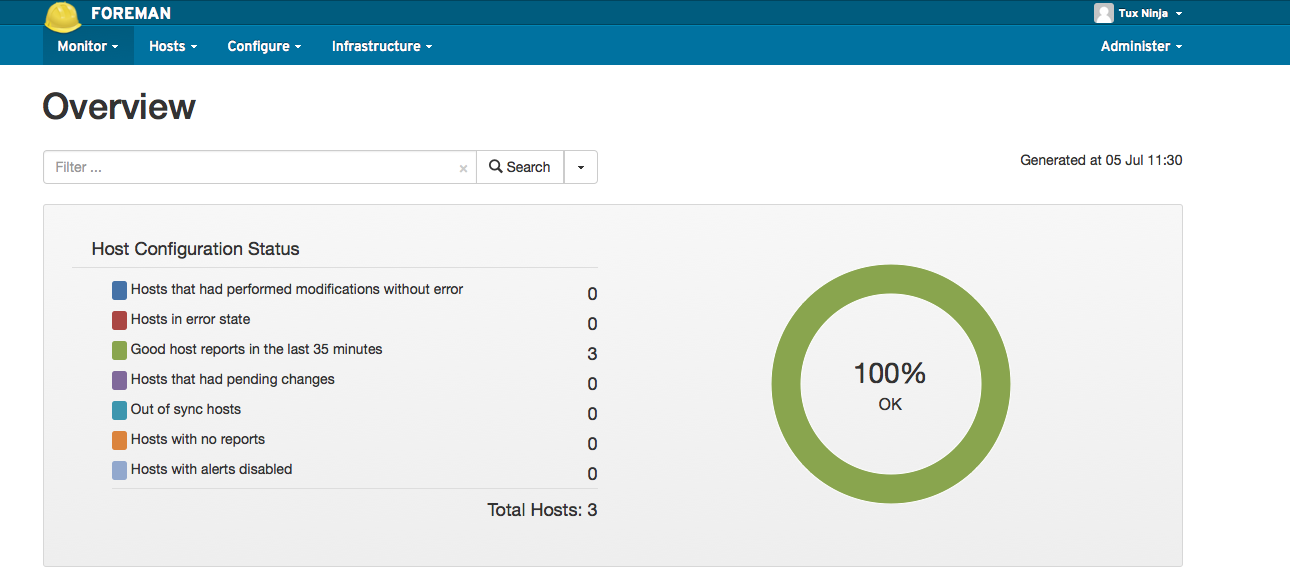
The Dashboard
Finally :-), If you have set everything up correctly you should be able to reach your console @ https://yourserversip.com or if you have DNS at the https://yourserversname.com (aka the FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name). Note the console uses SSL so you want to use HTTPS (on port 443 by default) not HTTP (which is port 80 by default), so just remember the HTTPS part and you should see a login screen, like this.
The first time Login is : admin and the Password is : changeme … make sure you do like the password says ! Also feel free to change you display name in your profile.
The End
Now that you have The Foreman installed. The next logical step is to install Openstack. I will cover that next time folks, I hope this helps out !

You must be logged in to post a comment.